Candida is a naturally occurring fungus. When overgrown, it can cause an infection on the skin and in the nails.
This infection is called candidiasis. Men, women, and children have Candida, and everyone can get an infection. But what is Candida, what are the symptoms of infection, treatments, and how can infection be prevented?
What is Candida?
There are over 150 types of Candida. The most frequently seen species is Candida albicans. The 15 known Candida albicans species are responsible for infections on the skin and in mucous membranes throughout the body. Overgrowth occurs more often in moist areas of the skin. Candida infections can range from minor infections that are treated with over-the-counter medications to very serious conditions that need care from a physician.
What causes candidiasis?
Skin infections are caused by warm, wet environments. Humid weather, poor hygiene, and tight clothing that rubs and doesn’t breathe well can increase the chances of candidiasis. Antibiotics can also alter the body’s natural Candida, causing an infection to occur.
Candidiasis of the nails can be caused by certain jobs. For instance, those that work with irritating substances, or people who are constantly in water have an increased risk of the condition. Brittle nails can also be caused by genetics and ageing. Women experience nail fungus more often than men do.
Symptoms of candidiasis
Candidiasis of the skin can have visual signs such as redness, rash, scaling, and swelling. These signs are often found where skin touches skin as well as areas that are more difficult to keep dry.
Some examples of these sensitive areas include:
- Folds of skin
- Under the breast
- Groin
- Armpits
- Spaces between fingers and toes
- Foreskin of an uncircumcised penis
The infection will most likely itch and feel uncomfortable if not treated.
Signs of candidiasis of the nails are nails that are brittle, easily breakable, or splitting. There are often white or yellow spots under the affected nail. These symptoms can live in fingernails or toenails and can be very painful. If untreated, the infection can make the nail thicker and even more discoloured. Athletes’ foot, the fungus that can spread between the toes and feet, may also occur at the same time.
Treatment for candidiasis of the skin and nails
To increase the likelihood of a quick recovery, keeping the skin dry is a necessary step. This may be more difficult in certain areas of the body. Powders can decrease moisture during and after recovery. It is important to see a dermatologist if the condition doesn’t improve after taking these actions. Prescription medication may be needed. Severe skin infections, often caused by invasive candidiasis, need to be treated by a doctor. Invasive candidiasis is a serious yeast infection that affects the blood, heart, eyes, brain, and bones.
People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV, are more likely to be affected by these invasive infections. Patients should seek medical attention immediately to be hospitalised.
Nail infections can be tricky to resolve. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends three steps in treating Candida of the nails:
- Examining possible underlying medical causes of the condition and correcting those issues if they exist.
- Keeping nails dry from harsh substances or water. Wearing gloves to do daily duties may help the condition.
- Treating nails by strengthening them. Petroleum jelly or thicker-based lubricants are better than watery lotions.
- If a nail infection cannot be treated, surgical nail removal may be the best option. A new nail will grow, but it is a slow process.
- Vitamin B with biotin may also help brittle nails, but it is a long-term solution and something that should be kept up as a daily supplement. If the condition doesn’t subside, it is best to talk to a skin specialist about a prescription drug to help with the problem.
Preventing candidiasis of the skin and nails
Prevention is extremely important in keeping the nails and skin healthy. One way to reduce a Candida infection is to lower the amount of sugar consumed. Keeping blood sugar at healthy levels can contribute to healthier skin and nails. This is especially important for people with diabetes.
It is extremely important to keep the skin and nails dry and clean. Changing sweaty or wet clothing, washing with soap, and drying well will help avoid the spread and increase of yeast. As for the hands and feet, choosing a reputable nail salon will decrease the chances of bacteria moving from customer to customer. It is also important to wear flip flops in public places like pools and showers.
Both the skin and nails have Candida, but balance is important. If a fungal infection does occur, home or over-the-counter remedies can be used. People with weakened immune systems, diabetes, or other health conditions may need medical care more immediately. If a fever and rash are present, that’s a sign that a doctor should be contacted right away.
Nail fungal infection: Causes, treatment, and symptoms
Also known as onychomycosis and tinea unguium, nail fungal infections are the most common diseases of the nails, making up about 50 percent of nail abnormalities. Fungus is normally present on the body, but if it overgrows, it can become a problem. Both fingernails and toenails are susceptible to infection, which usually appears as discoloration and thickening of the nail, and crumbling edges. The condition most commonly occurs in toenails.
Around 10 percent of the adult population suffers from nail fungus infection. Here we will provide an overview of nail fungal infections, in addition to common causes, treatments, and symptoms.
Fast facts on nail fungal infection
- Microscopic fungi in the nail cause the condition.
- It can affect both fingernails and toenails but is more common in feet.
- Diagnosis is carried out by examination of the debris under the nail.
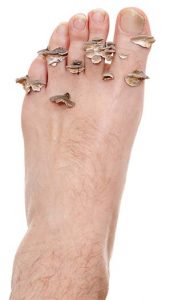 What causes nail fungus infections?
What causes nail fungus infections?
Microscopic organisms called fungi cause nail fungal infections; they do not require sunlight to survive so can thrive in these areas.
Most commonly, a group of fungi called dermatophytes (such as Candida) is responsible for nail fungal infections. However, some yeasts and moulds also cause these infections. Pathogens that cause nail fungus infection usually enter the skin through tiny cuts or small separations between the nail and nail bed. The fungi grow when the nail provides a suitably warm and moist environment.
Who is at risk for nail fungus infections?
Anyone can get a fungal nail infection, but they are more common in men than women and the elderly than the young. Some additional traits or factors raise the risk of nail fungal infection, these include:
- diminished blood circulation
- slow growing nails
- a family history of fungal infection (genetics)
- heavy perspiration
- humid or moist work environment
- wearing artificial nails
- wearing socks and shoes that prevent ventilation
- walking barefoot in damp public places (swimming pools, gyms, and shower rooms)
- previous injury or infection to the skin or nail
- diabetes, AIDS, circulation problems, a weakened immune system
- tight footwear with crowding of toes
- exercise that causes repeated minor trauma to the hyponychium (where the finger tip attaches to the nail)
Older adults are the most at risk of nail fungus infections as lower blood circulation and slower growing nails are part of the natural aging process.
What are the symptoms of nail fungus infections?
Nails that are infected with fungus typically are:
- thickened
- brittle
- crumbly
- ragged
- distorted
- dull
- darker or yellowish in colour
There may be also be:
- scaling under the nail – hyperkeratosis
- yellow or white streaking – lateral onychomycosis
- yellow spots at the bottom of the nail – proximal onychomycosis
- infected nails may separate from the nail bed – onycholysis
Nail fungal infections can result in pain in the toes or fingertips, and they may even emit a foul odour. Another symptom associated with nail fungus infections are fungus-free skin lesions called dermatophytids. These may appear like rashes or itchiness in an area of the body that is not infected with the fungus – much like an allergic reaction.
Nail fungus infection treatments
Treating nail fungus infections can be a long and expensive process. There are oral antifungal medications, topical ointments, and alternative therapies. Over the counter creams and ointments are available, but they have not proved very effective.
Topical nail fungus treatments can clear nail fungal infections, but often do not completely cure the infection. Alternative medicines used to treat nail fungal infections include Australian tea tree oil and grapefruit seed extract. However, there is no scientific evidence supporting the use of these products. In some extreme cases, a physician will opt to remove the entire nail.
Prevention of nail fungus infections
Preventing nail fungus infections requires hand and foot hygiene. Some suggestions include:
- Keeping nails short, dry, and clean.
- Wearing socks that breathe, usually synthetic.
- Using antifungal sprays or powders.
- Wearing rubber gloves to avoid overexposure to water.
- Refraining from picking or biting nails.
- Wearing shoes or sandals in public places and pools.
- Ensuring that your manicure or pedicure salon properly sterilizes tools.
- Using artificial nails and nail polish less often.
- Washing hands after touching infected nails.
- Avoiding sharing shoes and socks.