Adults may be affected with many different types of eye problems. The more common ophthalmic problems are cataracts, dry eyes, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy.
It is important to be aware of these conditions and to seek treatment early as timely intervention and preventive measures may help prevent loss of sight and the associated negative impact on quality of life that the visual impairment brings.
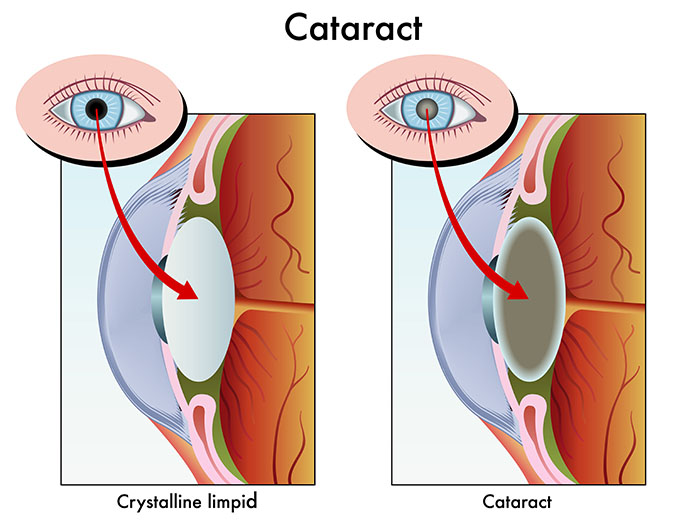
1. Cataract
A cataract is a clouding of the eye’s natural lens. Although it is common to have cataracts as we age, it is also more often seen in people who smoke, those who do not protect their eyes from the sun, diabetics and those with family history of cataracts. Trauma to the eyes and head may also cause cataracts.
Symptoms:
- Blurry or dim vision
- Glare
- Difficulty in night vision
- Seeing halos around lights
- Need for frequent changes in glasses
As the cataract worsens it severely affects the vision and surgery would be necessary to remove the cloudy lens and replace it with a new one. Most cataract surgeries are daycare procedures performed under local anaesthesia. With modern techniques, the end results are usually excellent.
2. Dry eyes
Tears function to lubricate our eyes and stops the surface from drying. Dry eyes occur if tears are not produced in the correct amounts or if it does not stay on the surface of the eye long enough. Dryness can range from mild afflictions to sometimes severe dryness that can damage the surface of the eyeball. Dry eye can affect anyone of any age but is more common as we get older. Dry eye is common in postmenopausal women and in people with systemic conditions such as certain types of arthritis.
Symptoms:
- Grittiness or itchiness of the eyes
- Pain and tearing in more severe cases
- Increased sensitivity to light
- Redness
- Discharge or stringy mucous
- Blurring of vision
There is no cure for dry eye, but its symptoms can be alleviated. Treatment include artificial tears, punctal plugs, warm compresses and newer therapies such as thermal pulsations and intense-pulsed light therapy.
3. Age related macular degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (ARMD) is a condition affecting older people, and it involves the loss of the person’s central field of vision. Globally, ARMD ranks third as a cause of blindness after cataract and glaucoma. Age is the biggest risk factor for developing ARMD. Family history, high blood pressure and smoking are other risk factors.
Symptoms:
- Maybe asymptomatic in the early stages
- Gradual or sudden blurring of vision
- Visual distortion especially straight lines
- Difficulty in recognising faces or central scotomas
People with macular degenerations can be treated with supplements, photodynamic therapy and anti-angiogenic drug injections.

4. Glaucoma
Glaucoma refers to a group of diseases that causes damage to the optic nerve with associated visual field loss. An elevated intraocular pressure is one of the primary risk factors for glaucoma. Advanced glaucoma leads to severe vision impairment and even blindness. Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness. Risk factors for glaucoma include age, family history of glaucoma, chronic usage of steroid medications, diabetes, hypertension and short-sightedness.
Symptoms:
- Called the ‘Silent thief of sight’, most people with open angle glaucoma usually do not have any symptoms until the disease is at an advanced stage. The disease starts affecting the peripheral vision and then progresses gradually to involve the central vision.
- Acute angle closure causes sudden eye pain, blurring of vision, eye redness, haloes, headaches, nausea and vomiting.
Although there are different types of medication that are used in the treatment of glaucoma, surgery maybe indicated in the cases which deteriorate despite optimal medical treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent worsening of the condition.
5. Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a specific complication of diabetes mellitus. Diabetic retinopathy develops with time and is associated with poor control of blood sugar, blood pressure, and blood lipids. It causes abnormal changes in the retinal blood vessels causing leakages, swelling of the retina and bleeding.
Symptoms:
- Maybe asymptomatic in the early stages
- Blurring of vision that maybe gradual or rapidly worsening
- Fluctuation in visual acuity
- Distortion of central vision
- Floaters
- Flashes of light
Treatment of diabetic retinopathy consists of strict control of blood sugars, laser photocoagulation, anti-vascular endothelial growth factors (anti-VEGF) injections and surgery.
EYECARE TIP
- Get your eyes checked if you have any of the symptoms mentioned above it is important to consult an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
- If you have significant medical or family history such as diabetes or glaucoma, it is advisable to see an ophthalmologist at least yearly.
Stopping by and getting your eyes checked in eye screening booths in malls and events can also help to detect eye problems early.
 Article by:
Article by:
Dr Palanyraj Naicker
Consultant Ophthalmologist
Columbia Asia Hospital – Cheras


